The Digital Games Market
Over the past decade, the digital games industry has experienced exponential growth, transforming from a niche entertainment sector into a cornerstone of the global economy. In 2015, the global gaming market was valued at approximately $91.5 billion. By 2025, this figure is projected to surpass $522 billion, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.25%.
In the United States, the video games industry has become a significant economic contributor. As of 2025, the market size is estimated at $107.6 billion . While specific figures for the European Union are less readily available, Europe’s e-commerce market, which includes digital games, is projected to reach $632.7 billion in 2024, with an annual growth rate of 9.09% expected from 2024 to 2029 . This underscores the substantial role digital games play in the EU’s digital economy.
Digital Trade War – The Catalyst: U.S. Tariffs and Global Trade Tensions
On April 2, 2025, President Donald Trump announced sweeping tariffs, imposing a 10% baseline duty on all imports and higher rates on specific nations, including a 20% tariff on European Union products . This move, described by Trump as “Liberation Day” for U.S. trade policy, aims to rectify perceived trade imbalances . The tech industry, heavily reliant on global supply chains, faces significant disruptions. Major companies like Apple, Amazon, and Meta have already experienced stock declines in response to the tariffs .
EU’s Potential Response: Digital Services Taxes and Tariffs on games
With Trump’s April 2, 2025 tariffs hitting European imports with a 20% duty, the European Union is weighing its response. While past trade disputes often centered on industrial goods like steel and automobiles, the 2025 tariffs take a broader approach, affecting tech industries and rekindling tensions around U.S. digital dominance in Europe.
As a result, EU policymakers are considering countermeasures that target the U.S. tech sector, particularly digital services, where American companies dominate the European market. Two primary strategies are being discussed:
Expanding the Digital Services Tax (DST)
The Digital Services Tax (DST) is an existing policy mechanism that taxes the revenue of digital platforms based on where their users are located, rather than where the company is headquartered. This tax was first introduced by individual EU member states as a way to counteract tax avoidance by major U.S. digital companies like Google, Meta and Amazon
Current Status of the DST
- Countries like France (3%), Spain (3%), and Italy (3%) already apply DST on revenues from digital services like advertising, marketplace commissions, and user data monetization.
- The OECD and G20 have been negotiating a global tax framework that would replace individual DSTs, but progress has stalled.
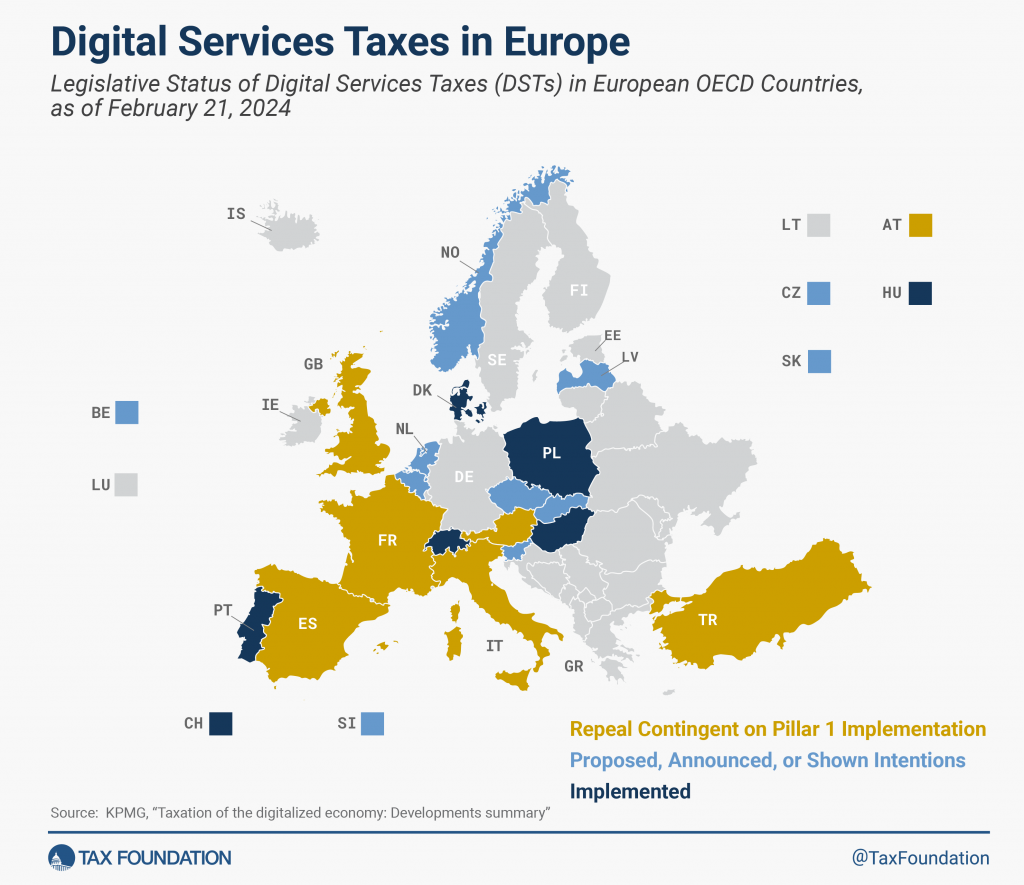
This strategy is seen as more politically feasible than direct tariffs because it aligns with existing EU efforts to regulate big tech under the Digital Markets Act (DMA) and Digital Services Act (DSA).
How an Expanded DST Could Target U.S. Tech
If the EU broadens its DST, it could:
- Increase the tax rate from 3% to 5%-7%, hitting U.S. firms harder.
- Expand the scope to cover video game platforms (Steam, Epic Games), subscription services (Patreon, Twitch), and cloud gaming (NVIDIA GeForce Now, Xbox Cloud Gaming).
- Apply the tax across all 27 EU member states, rather than a handful of individual countries.
Economic Impact of an Expanded DST
- U.S. tech companies would pass on higher costs to European consumers and developers, likely resulting in higher game prices, subscription fees, and content creator deductions.
- European gaming companies might benefit slightly by facing less aggressive competition from U.S. giants, but they, too, rely on platforms like Steam and Patreon for distribution.
- Potential pushback from European consumers and businesses, as they depend heavily on U.S. digital infrastructure.
Imposing Tariffs on Digital Transactions (Digital Tariffs)
While DST targets revenues, the EU could go further by imposing direct tariffs on cross-border digital transactions—essentially a tax on purchasing digital goods and services from non-EU companies.
How Digital Tariffs Could Work
- Apply a percentage-based duty (e.g., 5%-10%) on video game purchases, streaming services, and digital subscriptions originating from U.S. companies.
- Levy import fees on digital purchases from U.S. firms, affecting Steam, Epic Games Store, Netflix, Patreon, and Apple’s App Store.
- Charge European businesses extra for advertising on U.S. platforms like Google, Meta, and Twitter.
Despite these hurdles, a digital tariff would be a powerful bargaining chip in EU-U.S. trade negotiations.
Impact of Digital Tariffs
- Price increases for consumers: Games on Steam and Epic Games Store could become 5%-10% more expensive for EU users.
- Boost to European platforms: Companies like GOG (Poland), Ubisoft Connect (France), and European streaming services could see increased market share as consumers look for cheaper alternatives.
- Strong U.S. backlash: The Biden-Trump tariff wars in 2018-2020 showed that the U.S. is likely to retaliate aggressively if the EU targets its digital economy.
However, implementing digital tariffs poses logistical challenges:
- The WTO moratorium on e-commerce tariffs prevents digital taxes on cross-border online transactions—but the EU could argue this doesn’t apply to retaliatory tariffs.
- Technical enforcement is complex: Unlike physical goods, digital transactions don’t cross traditional borders, making tariffs difficult to track and collect.
- Potential legal battles between the EU and U.S. tech firms, leading to prolonged uncertainty.
How Would This Impact U.S. Digital Platforms?
Should the EU implement these measures, U.S. digital platforms operating in Europe could face increased operational costs. Steam, a leading digital distribution service for video games, might be compelled to adjust pricing structures, potentially reducing sales volumes. Similarly, Patreon, which facilitates content monetization for creators, may experience decreased patronage due to higher service fees. These changes could inadvertently benefit European-based platforms, as consumers and creators seek more cost-effective alternatives.
If the EU expands DST and/or imposes digital tariffs, the biggest losers would be U.S. tech giants.
1. Steam (Valve Corporation)
- Faces higher taxation on its European sales, potentially leading to increased game prices.
- Might rethink its market strategy by offering region-specific deals or shifting investment to other regions.
- European competitors like GOG (Poland) and Ubisoft Connect (France) could attract more European players.
2. Patreon & Other U.S.-Based Creator Platforms
- Higher service fees for European creators could drive them to EU-based alternatives or direct payment models.
- European competitors like Ko-Fi (UK) might see an increase in usage.
3. Subscription-Based Services (Netflix, Game Pass, YouTube Premium)
- A 5%-10% tax on digital subscriptions could make services like Xbox Game Pass and Netflix significantly more expensive in Europe.
- European streaming platforms like SkyShowtime (UK) and Molotov TV (FR) could gain market share.
Would This Boost Sales on European-Based Platforms?
However, the dominance of U.S. platforms in the global market presents a significant barrier to this shift. Companies like Steam have established extensive user bases and brand loyalty, making it challenging for European alternatives to capture significant market share quickly. Additionally, the network effects inherent in platform economies mean that users are more likely to remain with services where their communities are established.
Not necessarily—despite potential advantages for European digital platforms, U.S. tech firms still dominate the global market because of:
- User loyalty & network effects – European gamers and creators are deeply embedded in U.S. ecosystems (e.g., Steam libraries, Patreon support bases).
- Superior infrastructure & content – U.S. platforms invest billions in cloud services, game hosting, and digital rights management.
- Lack of strong European alternatives – While platforms like GOG, Green Man Gaming, Ko-Fi and yes even SpicyGaming exist, they don’t have the same scale as U.S. giants.
Unless the EU invests in homegrown digital marketplaces, U.S. firms will likely remain dominant, albeit at higher costs for European consumers.
U.S. Response: Escalation or Negotiation?
If the EU targets U.S. digital services, Washington is almost certain to retaliate:
- Trump’s administration could impose additional tariffs on European digital firms or game publishers (Ubisoft, CD Projekt Red, Paradox Interactive).
- New restrictions on European tech investments in the U.S.
- Legal battles at the WTO and OECD over unfair taxation.
How Likely Is the EU to Take This Course of Action?
Given the EU’s historical commitment to multilateralism and measured responses, it is likely that any countermeasures will be carefully calibrated to avoid unnecessary escalation. The EU’s consideration of targeting U.S. digital services aligns with its broader strategy of addressing the dominance of non-European tech giants and promoting fair competition within its digital market . However, internal divisions among member states and the potential economic fallout may temper the EU’s response
Do you like what we at Spicygaming do? Support us on Patreon.
✅ Why the EU Might Proceed
✔️ The EU has been frustrated with U.S. tech dominance and may use this as an opportunity to strengthen its own digital economy.
✔️ Several EU countries already tax digital services—expanding this tax would be a logical next step.
✔️ It’s politically popular in Europe to tax foreign tech giants, as it aligns with EU consumer protection policies.
❌ Why the EU Might Hold Back
✖️ Potential U.S. Retaliation: The Trump administration could escalate
✖️ Legal Uncertainty: If WTO rules continue banning e-commerce tariffs, digital duties could be challenged.
✖️ Harm to EU Consumers: Higher prices could reduce digital sales and anger European gamers and businesses.
So how likely is it?
Full-scale trade war with the U.S.: UNLIKELY – The EU prefers negotiation over confrontation, but escalating U.S. tariffs could force its hand.
Expanding DST: HIGHLY LIKELY – This aligns with EU goals of regulating Big Tech and closing tax loopholes.
Imposing Digital Tariffs: MODERATELY LIKELY – While politically appealing, enforcement and WTO rules pose challenges.
Don’t Miss
Conclusion – Will games become more expensive?
The imposition of U.S. tariffs has set the stage for a complex interplay of economic strategies and retaliatory measures. The digital games market, a significant contributor to both U.S. and EU economies, finds itself at the nexus of these developments.
The EU’s potential countermeasures against Trump’s tariffs could reshape the global digital economy, particularly in gaming and streaming services. While the expansion of DST appears highly probable, tariffs on digital goods remain a contentious and risky move. Should the EU impose higher taxes on U.S. platforms, the gaming market in Europe may experience significant disruptions, with price increases, market shifts, and heightened geopolitical tensions.
The key question remains: Will the U.S. retaliate further, deepening the digital trade conflict? If so, we could see a full-scale digital trade war that impacts consumers, developers, and tech companies on both sides of the Atlantic.






